Titanium Ilmenite ore dryer rotary drying equipment China staurk
Condition:New for sale , China
Origin:China Ilmenite ore dryer
Daily Capacity:40-1400 TPD per set
Drying Temperature:720- 980℃
Feeding Moisture:30% - 65%
Final Moisture:8-15% (adjustable)
Used for:Drying various titanium ores, as well as iron, vanadium, cobalt, nickel, copper, chromium, gallium, manganese, niobium, tantalum, scandium, selenium, tellurium, sulfur, tremolite
Titanium Ilmenite ore dryer rotary drying equipment China staurk
Ilmenite ore dryer alao called Titanium ore dryer is mainly composed of a heat source, a feeding machine, a feeding machine, a rotary drum, a discharging machine, a induced draft fan, an unloader, and an electric control cabinet. Coal, gas, oil, biomass and other fuels can be selected according to the user's operating conditions, which have the advantages of high thermal efficiency and large processing capacity.
Application
Used to dry various titanium ores, as well as iron, vanadium, cobalt, nickel, copper, chromium, gallium, manganese, niobium, tantalum, scandium, selenium, tellurium, sulfur, tremolite, zircon, apatite, garnet, and so on.
Working principle
After the material is fed into the cylinder from one end of the titanium ore dryer, it is evenly distributed and dispersed in the dryer under the flipping of the plate reader, and fully contacts with hot air to accelerate drying heat transfer and mass transfer. Thereby achieving the purpose of drying.
Features
1. High degree of mechanization, large production capacity, and continuous operation capability
2. Strong adaptability to material characteristics, low resistance to material passing through the cylinder, and low consumption
3. Various materials such as stainless steel and Q235 steel can be used for equipment manufacturing
4. Adopting a new type of feeding and discharging device to eliminate phenomena such as feeding blockage, discontinuity, unevenness, and material return
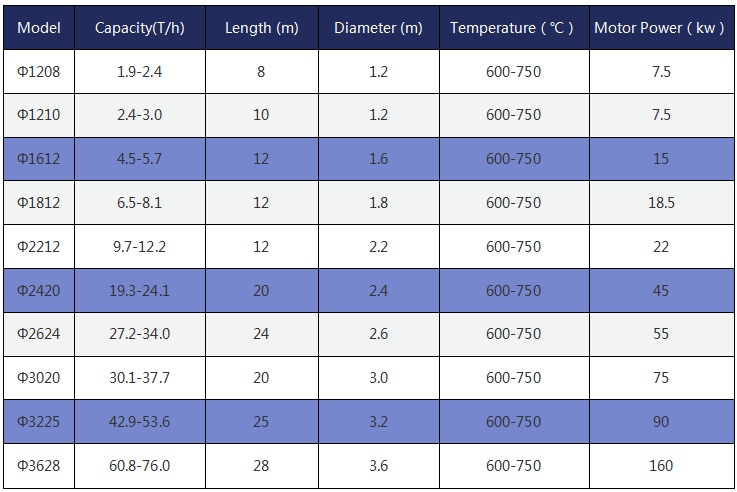
Parameter of the Ilmenite ore rotary dryer
Ilmenite ore and titanium introduction
Ilmenite ore and titanium oxide minerals, also known as titanium magnetite, are gray to black in color and have a slight metallic luster. They can be subdivided into rock minerals and sand minerals.
Titanium ore deposits are mainly composed of polymetallic coexisting minerals, which not only contain a large amount of iron, titanium, and vanadium, but also elements such as cobalt, manganese, niobium, tantalum, scandium, selenium, tellurium, nickel, copper, chromium, gallium, and sulfur
The TiO2 grade of titanium concentrate selected from rock ore is generally 42% -48%, while the TiO2 grade of titanium concentrate selected from sand ore can exceed 50%.


